Sloth fever has recently emerged as a topic of interest, particularly in relation to new and potentially dangerous diseases. Despite its seemingly benign name, sloth fever is a serious condition that warrants attention, especially in regions such as the USA where cases have been reported. This article explores the concept of sloth fever, its symptoms, causes, and the broader implications of the virus associated with it.
What is Sloth Fever?
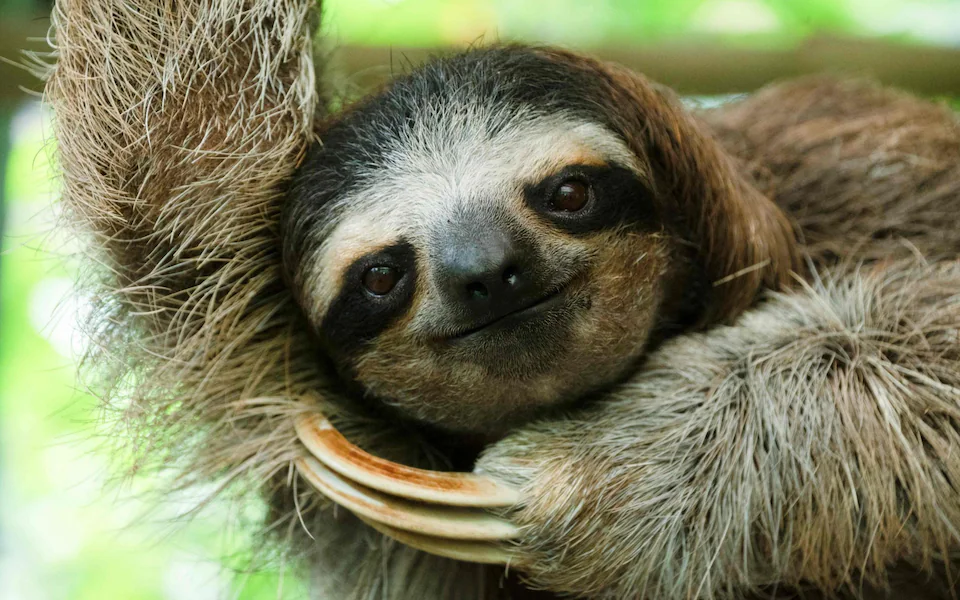
Sloth fever refers to an illness caused by a specific virus believed to be transmitted from sloths to humans. These animals, native to Central and South America, are known for their slow, deliberate movements. However, close human interaction with sloths, whether in the wild or captivity, has raised concerns about the potential spread of zoonotic diseases—illnesses that jump from animals to humans.
The sloth fever virus is still under investigation, with researchers trying to trace its origins, transmission methods, and its impact on human health. Although the chances of humans coming into contact with sloths are relatively low globally, increased tourism, the handling of sloths in captivity, and human encroachment on wildlife habitats have heightened the risk of virus transmission.
Sloth Fever in the USA
While sloth fever is primarily associated with regions where sloths are naturally found, there have been isolated reports in the USA. These cases are typically connected to individuals who have traveled to areas where sloths live or have had direct contact with sloths in captivity. The presence of sloth fever in the USA has sparked concerns among health officials about the potential for wider transmission.
So far, sloth fever in the USA has remained limited to isolated incidents, with no widespread outbreaks reported. However, the possibility of the virus becoming a significant public health issue persists, especially as more people engage with sloths through tourism, pet ownership, or conservation efforts.
What is Sloth Fever? A Deeper Look
Sloth fever presents a variety of symptoms that can range from mild to severe. In some cases, individuals may experience symptoms that resemble those of common illnesses like the flu or a cold. In more severe cases, the infection can lead to complications that require medical attention.
The sloth fever virus is thought to primarily affect the respiratory and nervous systems, leading to a range of symptoms including fever, muscle aches, fatigue, and respiratory distress. In rare instances, sloth fever can also cause neurological symptoms such as confusion, seizures, or even coma.
Sloth Fever Symptoms: What to Watch For
Recognizing the symptoms of sloth fever is critical for timely diagnosis and treatment. Symptoms can vary widely from person to person, but common indicators include:
- Fever: A sudden onset of fever is often an early sign of sloth fever.
- Muscle Aches: Pain in the muscles and joints is frequently reported.
- Fatigue: A persistent feeling of tiredness or exhaustion that is not alleviated by rest.
- Respiratory Symptoms: Coughing, shortness of breath, and difficulty breathing are signs of respiratory involvement.
- Neurological Symptoms: In severe cases, confusion, disorientation, or seizures may occur.
If you or someone you know has recently been in contact with sloths or has traveled to regions where sloths are common, and begins to exhibit these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. Early detection and treatment can prevent the progression of the disease and reduce the risk of severe complications.
Sloth Fever Virus: A Growing Concern
The emergence of the sloth fever virus is a reminder of the ongoing risks posed by zoonotic diseases. As humans continue to interact more frequently with wildlife and encroach on natural habitats, the likelihood of new viruses emerging increases. Sloth fever underscores the importance of maintaining a careful balance between human activities and the natural environment.
Health authorities are closely monitoring the situation and working to develop strategies to prevent the spread of sloth fever. This includes educating the public about the risks of handling sloths and other wildlife, as well as implementing measures to control the spread of the virus in affected areas.
Preventing Sloth Fever: What You Can Do
Preventing sloth fever primarily involves reducing the risk of exposure to the virus.
- Avoid Direct Contact with Sloths: If you are in regions where sloths are found, avoid handling these animals. Sloths, while appearing harmless, can carry viruses that pose risks to human health.
- Practice Good Hygiene: After any contact with sloths, thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water. Refrain from touching your face, especially your eyes, nose, and mouth, until your hands are clean.
- Exercise Caution in Captive Settings: When visiting zoos or wildlife sanctuaries, follow all guidelines and instructions provided by the staff. Avoid feeding or handling the animals, and keep a safe distance.
- Stay Informed: Keeping up to date with the latest information on sloth fever and other zoonotic diseases is essential. Awareness can help you make better decisions regarding interactions with wildlife.
The Future of Sloth Fever Research
As researchers continue to study the sloth fever virus, more will be learned about its transmission, origins, and impact on human health. Ongoing research efforts aim to develop diagnostic tools, treatments, and possibly vaccines to reduce the risks posed by this and other zoonotic viruses.
In the meantime, it is important to remain vigilant and take precautions to protect yourself and others from potential risks associated with sloth fever. By staying informed and practicing responsible interactions with wildlife, you can help prevent the spread of this virus and contribute to broader efforts to curb zoonotic diseases.
Conclusion
Sloth fever represents a growing concern as a result of increased human interaction with sloths, particularly in regions where these animals are native. The sloth fever virus poses potential risks to public health, especially in the USA, where cases have been reported. Understanding the symptoms and taking preventive measures are essential to minimizing the impact of this virus.
As research continues, it is hoped that more effective strategies for managing and preventing sloth fever will emerge. Until then, it is crucial to remain cautious and informed, particularly if you are in areas where sloths are present or involved in activities that bring you into contact with wildlife.





Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you. https://www.binance.com/lv/register?ref=B4EPR6J0
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
I gotta bookmark this website it seems very useful handy
This blog is definitely rather handy since I’m at the moment creating an internet floral website – although I am only starting out therefore it’s really fairly small, nothing like this site. Can link to a few of the posts here as they are quite. Thanks much. Zoey Olsen
Awsome post and straight to the point. I am not sure if this is in fact the best place to ask but do you folks have any ideea where to hire some professional writers? Thank you 🙂
Hello, Neat post. There’s a problem together with your site in web explorer, would test thisK IE still is the marketplace chief and a large portion of people will omit your excellent writing because of this problem.
very nice post, i actually love this website, keep on it
I have been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thanks, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your web site?
Hello! I just would like to give a huge thumbs up for the great info you have here on this post. I will be coming back to your blog for more soon.
I’m still learning from you, while I’m trying to achieve my goals. I definitely liked reading all that is written on your website.Keep the tips coming. I loved it!